Objectives
HARMONY main objective is to improve the recyclability of rare earth elements (REEs) permanent magnets from any waste flow, i.e. EoL wind turbines, electric motors and other Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). This objective is mainly achieved through the development of a full recycling process covering the NdFeB magnetsNdFeB magnets, also … More value chain, encompassing:
- the collection and dismantling of NdFeB magnetsNdFeB magnets, also … More,
- the production of powder through three technologies,
- the recovery of REE metals by an indirect recycling process,
- the production of recycled magnets via several industrial processes
- and the validation of the produced magnets in three high impact applications.
This project will be validated by a pilot implementation reaching a TRLs of 6-7 and demonstrating the economic, environmental and social viability of the close-loop recycling process. The main goal is to carry out a full exploitation plan with a commitment of the partners at the end of the project to achieve a future-full scale manufacturing planned for 2028.
Methodology
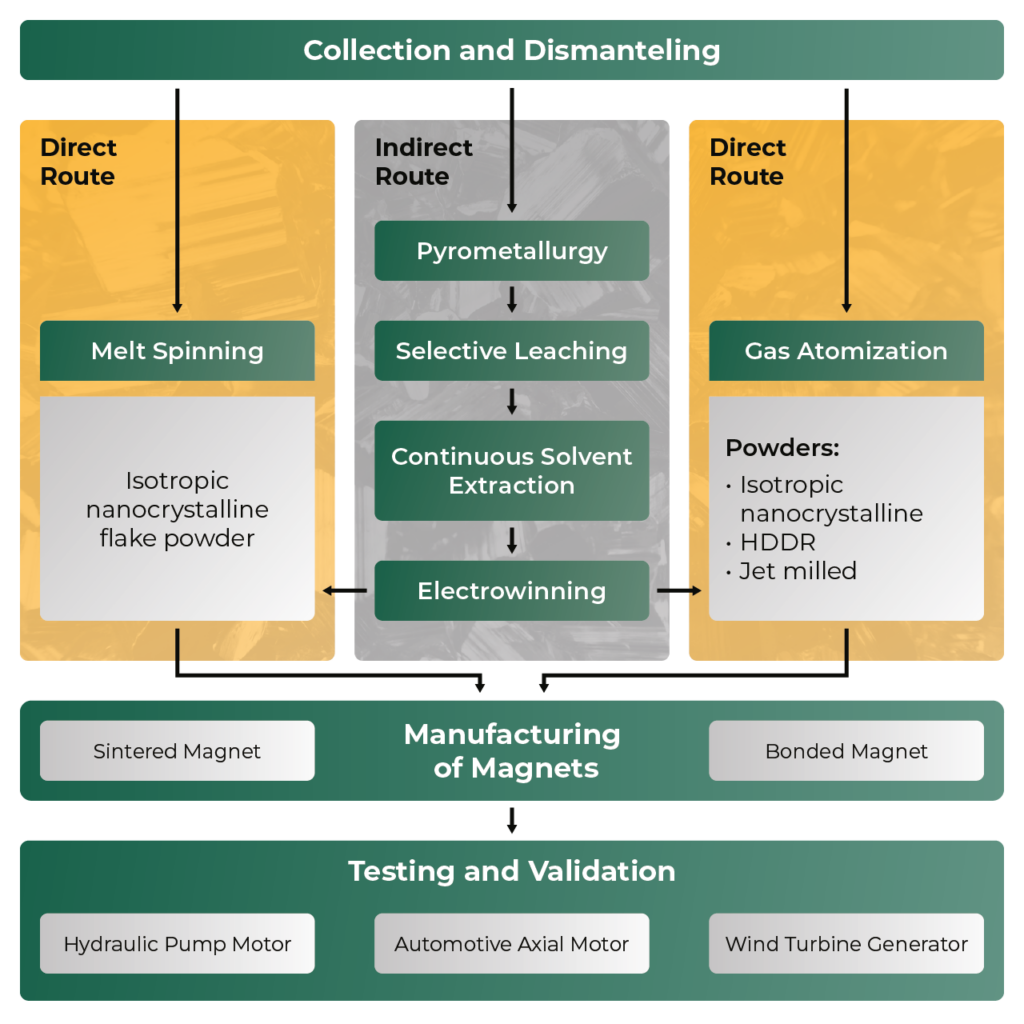
HARMONY project concept aims to develop and implement, at pre-industrial scale, a flexible and efficient NdFeB recycling process in order to close the value chain of PMs and strongly increase the independence access of Europe to Critical Raw Materials (CRMs). HARMONY will be mainly focused on the recyclability of NdFeB alloys using short-loop technologies and on the recovery of most common REEs (Nd, Pr, Dy and Tb) in NdFeB magnetsNdFeB magnets, also … More when direct recycling is not possible.
Different types of recycled powders will be produced through two type of methods: (a) direct methods, using gas atomization
Gas atomization … More, melt spinning or selectively leached HPMS powder and (b) indirect methods, encompassing innovative steps such as a pyrometallurgical concentration, selective leaching, solvent extraction refining and electrowinning. Both kinds of methods are complementary. This combination of direct and indirect recycling technologies will allow dealing with any scrap containing NdFeB in any form (sintered or bonded magnets), enhancing thus its recyclability.
Direct methods
Direct methods are those which reprocess the material directly from the alloy. This is possible when the scrap is not very much contaminated or oxidized, and well classified in batches of similar chemical composition.
Direct recycling methods include re-sintering, melt spinning, gas atomization
Gas atomization … More, HDDR process and recasting. Compared with indirect methods, they do not require so much energy and do not produce significant chemical wastes.
Indirect methods
In the indirect recycling route, recovery and refining of REEs will be carried out through a sequence of 4 stages.
- Firstly, the ferrous scrap will be processed via pyrometallurgy to obtain a slag while recovering feed related impurities as pig iron.
- Subsequently a selective leaching and precipitation process will be scaled up to produce a highly concentrated REEs salt.
- Next, the obtained REEs concentrate will be transferred for further purification and separation of individual REEs through its solvent extraction plant.
- The end product salt will be selected according to the final electrowinning process and purified into high grade REE metals.